In today’s increasingly digital world, cybersecurity is more important than ever. With the rise in cyber attacks and security breaches, there’s a growing need for well-trained cybersecurity professionals who can protect our personal information and critical systems.
Educators and instructors have a vital role in preparing students for these cybersecurity careers. However, teaching cybersecurity can be challenging due to its complex and constantly evolving nature. The key to success is engaging students in innovative ways to engage students that make the learning process both effective and enjoyable. This blog explores five cybersecurity education strategies for enhancing cybersecurity education, making it more accessible and engaging for students.
Relate Cybersecurity to Everyday Life
To truly engage students in cybersecurity classes, it’s important to connect the lessons to real-world issues and current cybersecurity threats. When students see the direct relevance of what they’re learning, they’re more likely to stay interested and committed to their studies.
- Talk about real-world examples: Use cybersecurity case studies based on recent data breaches or cyber incidents. Students can gain insights into effective cybersecurity strategies and learn from real-world examples by analyzing how security teams responded to these situations. For instance, discussing a high-profile phishing attack can help students understand the risks associated with phishing emails and the importance of implementing security measures to protect personal information.
- Discuss news stories that highlight the importance of cybersecurity: Bring current events into the classroom.Educators can discuss the latest cybersecurity threats, such as emerging cyber risks or new forms of cyber attacks. Thiskeeps students informed and encourages them to think critically about how they would respond to these challenges in their future careers. Incorporating news reports and articles about cybersecurity in various industries can also help students understand the broader impact of cybersecurity on society and the importance of cybersecurity education. This Keeps the material fresh, and shows cybersecurity is a real and ongoing concern.
- Make the topic more relatable to increase student interest: Ask students to think about their online habits, such as protecting their social media accounts or what they do when they receive a suspicious email. Relating the topic to their personal experiences can make learning more engaging and meaningful.

Use Interactive and Hands-On Learning
Traditional lectures might not be the most effective way to teach cybersecurity. Instead, try incorporating interactive cybersecurity resources like simulations, games, and hands-on activities to engage cybersecurity students. When students actively participate in real-world scenarios, they gain a deeper understanding of the material and retain information better. This approach makes complex concepts easier to grasp and prepares students for the challenges they’ll face in their careers.
- Encourage hands-on activities to develop practical skills: Use hands-on cybersecurity labs where students get to work directly with systems, such as configuring firewalls, analyzing network traffic, or conducting risk assessments. For example, students might work on tasks like setting up secure networks or responding to simulated cyber attacks. These hands-on practical cybersecurity training are crucial because they provide students with the skills to secure their devices and data.
- Use online simulations to mimic phishing attacks: Several platforms are available that simulate phishing scenarios and ransomware attacks. Students can participate in these cybersecurity simulations to learn how to identify and respond to phishing emails correctly. By simulating cyber attacks, students develop problem-solving skills and learn to make quick, effective decisions. This practical experience can help them recognize threats in the real world.
Boost Student Participation with Gamified Learning Strategies
Gamification in cybersecurity education is a powerful tool that can significantly enhance cybersecurity student participation and motivation. By integrating game-like elements into the curriculum, educators can increase student participation and keep them motivated to learn.
- Earning Points and Badges: Incorporating gamification allows students to earn points for completing assignments, participating in class discussions, or mastering specific skills. Additionally, students can earn badges as they achieve milestones in their learning journey, visually representing their progress and accomplishments. These can be tracked on leaderboards, adding a competitive element to the learning process.
- Cybersecurity Challenges: Organize cybersecurity challenges. These challenges involve solving puzzles, decoding messages, or defending against simulated cyber attacks. For example, educators can create a scenario where students must protect a network from cyber threats, encouraging them to apply their knowledge and think critically to handle risk management correctly. This can turn a potentially dry subject into an exciting challenge.
Encourage Collaboration and Group Work
Cybersecurity is often a team effort, and students need to develop the skills needed to work effectively with others. Collaborative learning in cybersecurity can be facilitated through group projects and team-based activities, which mirror the real-world scenarios students will encounter in their careers.
- Team-Based Cybersecurity Activities: Educators can organize team-based cybersecurity activities like ethical hacking competitions or vulnerability assessments. These activities encourage students to work together to identify and address security risks and learn to appreciate different perspectives to foster collaboration and shared responsibility.
- Have students create a cybersecurity plan for a fictional company: Have students work together to assess risks, develop security policies, and make an incident response plan. This exercise teaches them real-world cybersecurity challenges and the importance of teamwork and collaboration in the field, as they must communicate and coordinate with their peers to achieve their goals.
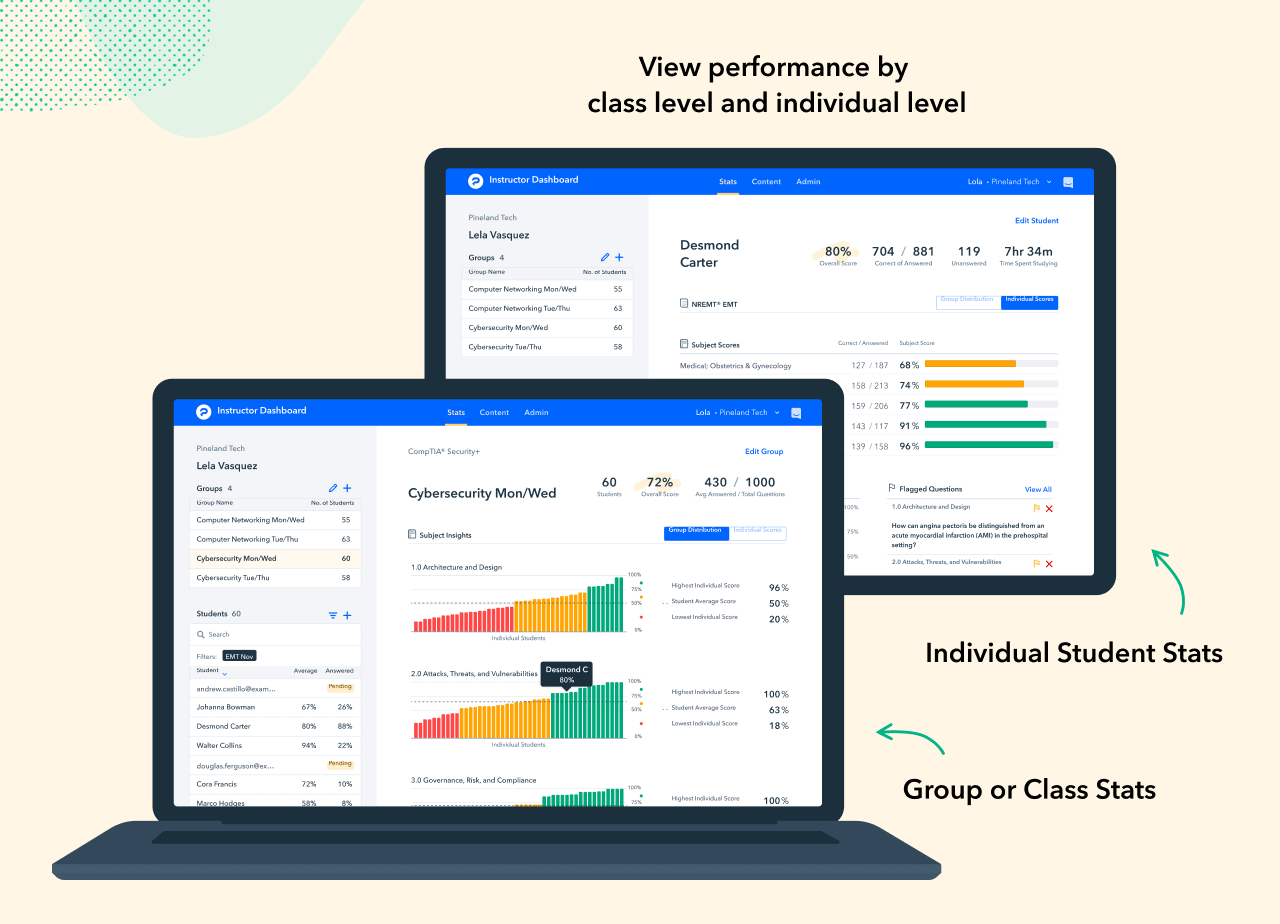
Leverage Online Tools and Interactive Resources
The digital nature of cybersecurity makes it ideal for integrating online tools and interactive resources into the curriculum. These tools enhance the learning experience and provide students valuable opportunities to practice and refine their skills.
- Online Tools for Cybersecurity Education: Educators can use online tools to facilitate learning and collaboration. For example, platforms like Pocket Prep offer practice exams that help students reinforce their knowledge and take quizzes even on the busiest of days.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): Use a Cybersecurity LMS platform like Pocket Prep to track student progress, administer assessments, and store important documents. This technology is a valuable resource for cybersecurity educators to support continuous learning and ensure students can access the resources they need to succeed.
- Digital Learning Platforms: Incorporating digital learning platforms like online labs allows students to practice cybersecurity skills in a virtual environment, where they can experiment with different techniques and strategies without the risk of causing real-world harm while helping students stay engaged with the material.
Preparing the Next Generation of Cybersecurity Professionals
As the demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals grows, educators play a crucial role in preparing the next generation. By adopting innovative teaching methods—such as hands-on labs, gamification, real-world case studies, collaborative projects, and interactive online tools like Pocket Prep—educators not only create an engaging and effective learning environment but also contribute significantly to the future of cybersecurity.
These strategies not only help students master complex cybersecurity concepts but also equip them with the practical skills needed to succeed in their future careers. Ultimately, by fostering a passion for cybersecurity, educators can inspire their students to become cybersecurity experts to defend tomorrow’s digital world.

